In Part 1 of this series I introduced Google webmaster tools and walked you through adding websites. Now that you have your site(s) in the system, you’ll need to configure your site so you get the most out of the data provided through the Webmaster Tools interface.
Site Configuration
Site configuration allows you to review and adjust your basic configuration settings. You don’t have a lot of leeway here but some of the very basics are covered which allow you to adjust how Google handles your site.
Webmaster Tools gives you four primary ways to configure your website:
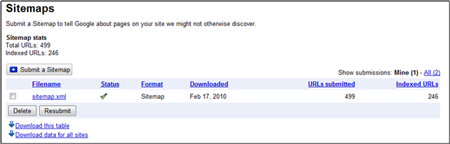
If you have an .xml sitemap for your website you can submit that to Google through Webmaster Tools. Once submitted, you’ll get stats such as when it was last downloaded, how many URLs were submitted how many site URLs are in the search index.
Each time your site changes, with new pages being added or removed, you should re-create your site map and resubmit it to Google. This ensures they have the most recent version to crawl.
If you’re showing a disproportionate number of URLs not being index from those submitted, this may represent a problem with your site map or the architecture of your site. Either way, it bears looking into.

This section allows you to see and edit Google’s access to your site via the robots.txt file. You can see when the robot.txt file was last downloaded by Google and what specifically it reads. Google also provides a way for you to create a new robots.txt file if you don’t have one.
Typically the robots.txt file is for telling the search engines what sections of the site you don’t want crawled and indexed but it’s good to have one even if to tell the engines they have the run of the house.
If you find specific URLs that Google is indexing that they shouldn’t you can either add that to your robots.txt file or submit that URL to Google directly through Webmaster Tools with the Remove URL link provided on this page.
The URL removal tool is only good for 90 days so if you want something permanent, use your robots.txt file. Here have the option to temporarily remove a single URL, a sub-directory of your site, your entire site, or the Google cache of a particular page.

You can also test your site against different Google Crawlers (User Agents) to make sure your site is accessible for image results, mobile results, and their AdSense and AdWords crawlers.

If, for whatever reason, your site isn’t allowing any of these crawlers access you’ll be notified here and can make changes as needed.
Site links are the additional links below your primary listing that Google chooses to give some websites. Here’s what my sitelinks look like in the search results:

Webmaster Tools will let you view and make edits to your sitelinks:

Using the “block” options Google allows you to ask that a particular site link not be used and provide a reason why.

Unfortunately you can’t ask to change the text of a sitelink without first blocking it entirely, which you may not want to do for a valuable site link, even if it reads incorrectly.

This section is used if you are changing URLs for your site. Obviously, changing URLs is not recommended, but if you do Google provides a nice way to give them notification… along with all the proper redirects being put in place behind the scenes.
This page mostly contains information on how best to move your site to a new domain and then allows you to select the new URL (after you’ve set it up in Webmaster Tools) to tell Google that the old domain is now the new domain.

Google allows you add some basic settings for your website that helps them know how best to crawl and index your site. Here you can adjust the following:
Geographic targeting: Select which country your site is aimed for. If you have a global TLD (.com, .net, etc) you can tell Google that your site is designed for a specific country audience. If your site is global then you won’t want to change these settings at all.
If you have section of your site in different languages you can set up each unique URL section in Webmaster Tools and assign the geographic location for that portion of the site.
Preferred domain: Do you want your site accessed with or without the www. in the URL? Consistency matters and unfortunately, many sites are inconsistent with their internal linking with some links pointing to www. URLs and others not. Short of fixing all your internal links, making them consistent throughout your site, you can tell Google your preference.
Even if you have all your internal links in order, set your preferred domain to account for any incoming links from external sites that may not be set up properly.
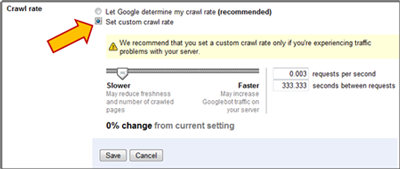
Crawl rate: Google allows some sites to change the crawl rate – the rate in which Google spiders your site. This can help you reduce the speed at which Google indexes your pages which can free up much needed bandwidth. In some cases Google will set a custom crawl rate for you and you won’t be able to make any edits here.
Parameter handling: Dynamic sites that us an inordinate number of parameters in the URLs can use this section of the site to tell Google which parameters make a difference and which should be ignored. This help keep bogus URLs or duplicate pages out of the Google index which can improve the site crawl and pages in Google’s index.

Learn more about these sections of Google Webmaster Tools
- Part I: Setting Up a Site
- Part II: Site configuration
- Part III: Your site on the web
- Part IV: Your site on the web (continued)
- Part V: Diagnostics
- Part VI: Labs

Pingback: SEO With Google Webmaster Tools – Part 1: Setting Up a Site » (EMP) E-Marketing Performance
Pingback: SEO With Google Webmaster Tools – Part 3: Your Site on the Web » (EMP) E-Marketing Performance