Link building expert Hamlet Batista dishes out a never-before revealed link building strategy:
When PageRank just isn’t enough: How to determine the true value of a link.
Not all links are created equal. We know that some links help more than others in getting high search engine rankings. For some time now, link builders have primarily relied on Google’s toolbar PageRank as a good measure of the quality of a link. Higher PageRank values were ostensibly better than lower ones. Unfortunately, Google has played so much with the PageRank values it displays that it has become increasingly less useful. Here’s why:
- The PageRank displayed is an approximation of the real PageRank. Google computes the real PageRank of a link at least once a month, probably sooner, but it purposely chooses to update the displayed PageRank only after several months. The last update took six months to happen.
- Google is reducing the visible PageRank of sites they catch selling or buying links. The real PageRank, however, has not been affected, as such sites report no drop in traffic or rankings.
- PageRank doesn’t mean much to other top search engines. They use their own link-based algorithms to evaluate the importance of a link.
- PageRank only measures the absolute importance of a page, but doesn’t tell us how much Google trusts a page. Search engines internally label pages as SPAM or not SPAM. Pages labeled as SPAM are not trusted and their links might carry negative weight.
There are already other, better methods in place to determine the value of links. Some of them take into account a multitude of factors, including number of links, indexed pages of a site, traffic, and so on. Those are all good measurement techniques, and I want to introduce a new one to your arsenal.
Crawl Rate and Indexing Rate
It is known that search engines use their link analysis algorithms not only to measure the importance of a page, but also to determine how frequently it should be crawled and indexed. Why? Important pages are seen by the general public the most. Search engines crawl and index important pages, say the New York Times home page, more frequently so that search results look up to date. By studying the crawling and indexing rate of a page we can have an indirect measure of its true value for link building.
To do this properly, though, we also need to consider how frequently the page gets updated, as that is another factor search engines consider when determining how often to crawl and index.
Determining the crawl rate of a page
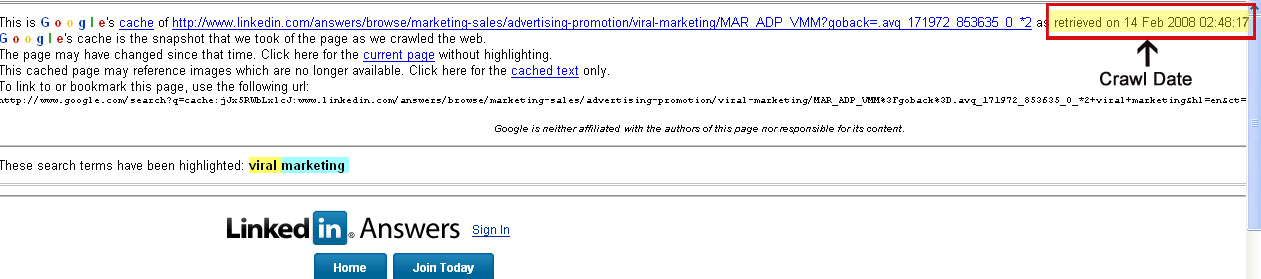
In order to determine the crawl rate of a page we need to monitor the search engine cache. The date of the cache is the date the page was crawled. The process of crawling involves downloading the page and storing it in a repository for further analysis. For example, if you see a page whose cache is several weeks or months old, you know that the link will not be very valuable. On the other hand, if a page has a cache date of Yesterday, it should be a good link. In reality, you need to look at the page at a later date when it has been crawled again to determine how many days/hours it takes in between crawls.
Determining the indexing rate of a page
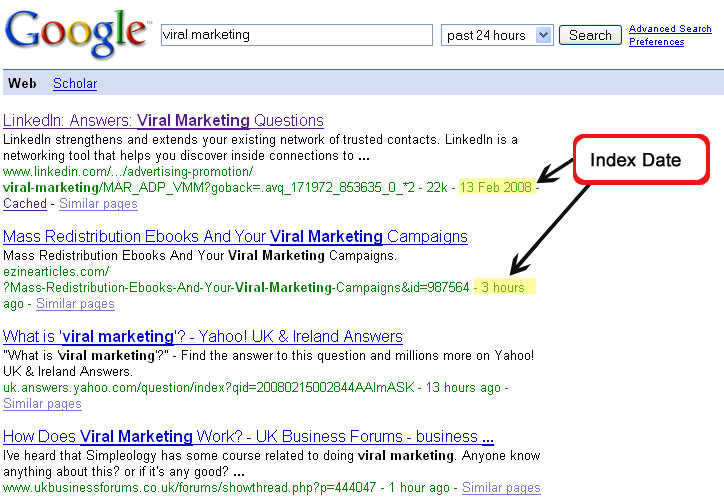
This is a technique you can do with Google. Ideally, pages should be indexed right after they are crawled, but that is not necessarily the case. Crawling is simply downloading pages, but indexing is a far more complex process that once upon a time took a full month to complete. It is fairly obvious to see on the SERPs that the process is an incremental one. Another reason to check the indexing rate is that some pages may be crawled but never indexed because the crawling process detected some duplicity. So, it is important to know when a page is indexed.
In order to check when a page was indexed, we can do an advanced search using the date range filter. When you specify a date, past 24 hours for example, Google will display the time the page was indexed. You can see that it is not the same time as when the page was crawled by clicking on the “cache” link. The cache date is logically sooner.
Same as with the crawl rate, you need to monitor the SERPs to see when the page is last indexed. That way you can see how frequently the page gets indexed.
Determining the update rate of a page
As I mentioned above, the crawl and indexing rate also depend upon how frequently the page author updates the page. Pages that are updated several times during a day are very likely to be crawled and indexed in hours instead of days. That is, of course, assuming that the page is deemed important by the search engine.
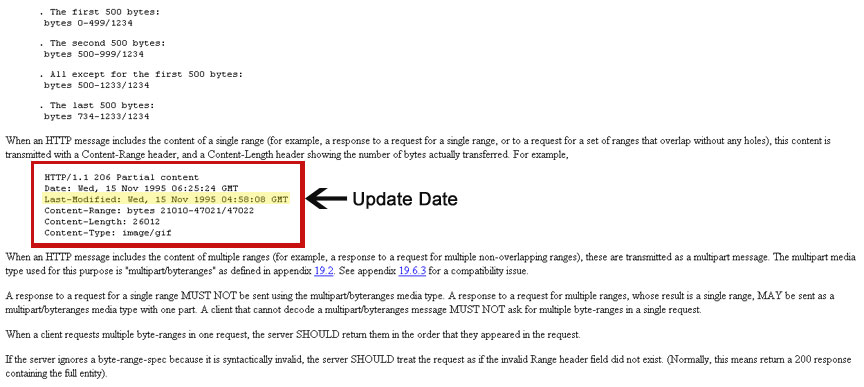
Instead of going to the page and hitting ‘Refresh’ every hour to see how frequently it gets updated, there is a simpler method used and supported by most search engines but not by most web hosting software: the last-modified and if-modified-since header combo, also known as conditional HTTP GET.
Conditional getting is a technical process designed to save bandwidth. If there have been no changes to a page, downloading it a second time is rather inefficient. In order to save bandwidth, popular browsers and search engine robots (including MSNBot) support conditional getting. When the browser/crawler pulls a page, the server returns a header (last-modified) that says when the page was last updated by the author. The second time the server will only return the page if it has been modified. If it has not, it will simply return a status code (3xx) to tell the browser client to come back later.
We can use this insight to determine how frequently a page is updated. We look at the last-modified header and by monitoring when it changes we can tell the rate at which the page gets updated by its author.
Putting it all together
Once you know these three rates, you can use the following matrix to determine the true value of the link.
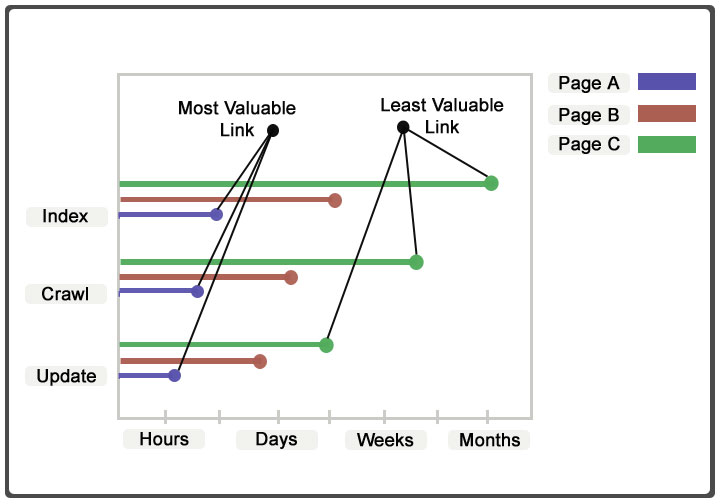 This technique is definitely more practical with a tool to automate the process. If there is enough interest, I might be able to make it public. Please let me know.
This technique is definitely more practical with a tool to automate the process. If there is enough interest, I might be able to make it public. Please let me know.
Hamlet Batista
Hamlet Batista dot Com